Real World IoT Use Cases
The number of use cases being touted by suppliers and developers appear to be endless, from simple ideas such as smart ice cube trays all the way to sensors being used to track environmental damage. In the following article, we take a look at some real-world use cases to see just a few of the ways that IoT is being leveraged today.
DIGITAL HOSPITALS
Humber River Hospital, Toronto, Canada
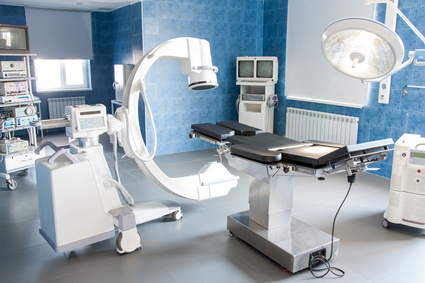
Toronto is looking to enhance the experience of patients by building North America’s first fully digital hospital which opened in late 2015. Barb Collins, the Humber River hospital’s chief operating officer says the digital transformation will result in “[faster care], it should be more accurate, and it should allow a better link between [medical records] and the practitioners caring for [the] patient”.[i] Here are some details on the new hospital:
- Patients will be able to control room temperature, lighting and have access to medical charts on a monitor by their beds.
- Patients will be able to communicate with nurses through a video chat or instant messaging system; this same platform can be used to communicate with family and friends.
- Vital signs will no longer have to be recorded manually by nurses. Instead, metrics will automatically be captured and stored digitally.
- A series of chutes and automated vehicles to deliver supplies such as medicine, bed sheets and food.
- Nurses will be able to order blood-work with a small device, reducing the chance of errors.
- Patients will be provided with wristbands for patient identification and confirmation the correct medications are given.
- The hospital should have 100% fresh air circulation and expects to use 40% less energy per year when compared to other hospitals.
Other digital hospitals have seen positive results. A hospital in Norway which went fully digital in 2008 says their patients stay on average 3-5 less days in the hospital.[ii] However, an entirely digital system can have drawbacks. The Oslo hospital has had their system fail three times, which resulted in all internet phone communication and medical records being inaccessible, thereby putting patient lives at risk.[iii]
SMART CITIES
Barcelona, Spain

Barcelona is aiming to become a reference for Smart Cities around the globe as they work to merge urban planning, ecology, and information technology to benefit the entire community. The long-term impacts of the initiatives is difficult to quantify because they are still in the early stages of the project. Regardless of positive or negative outcomes, Barcelona will surely serve as an example to other cities on what the best practices are and how to make improvements in other areas when future cities decide to implement similar initiatives.
The smart city programme in Barcelona includes seven initiatives (City Climate Leadership Awards):
- Smart Lighting. Remotely controlling street level lighting in addition to transitioning 50 streets and a total of 1,155 lampposts to LED technology.
- Smart Energy. Achieving greater energy efficiency be deploying more than 19,500 smart metres in the Olympic Villa.
- Smart Water. Remote irrigation for the city’s green spaces; 77 fountains are controlled thus far.
- District Heating and Cooling. Two networks provide hot water in 64 buildings which span an area of 21 km.
- Smart Transportation. Improving public transport efficiency by deploying orthogonal bus lines
- Zero Transmission Mobility. Plan to promote the use of electric vehicles by deploying electric charging stations, as well as electric vehicles fleets and car rentals; the city currently has more than 500 hybrid taxis, 294 public electric vehicles, 262 recharging points, 130 electric motorbikes and an estimated 400 private electric vehicles on the streets
- Open Government. Making municipal government activities more transparent to its citizens, beginning with the deployment of 44 “citizen’s attention” kiosks and the launch of an Open Data portal.
SMART AGRICULTURE
Dolphin Engineering – Lugano, Switzerland
Libelium – Zaragoza, Spain
Disease and pests can have a substantial impact on grape production at vineyards, resulting in large economic damage. Then in an attempt to reduce economic damage, growers use treatment methods which create ecological damage. It is unfortunate these traditional treatment methods incur large costs for growers and are largely inefficient.
Dolphin Engineering, in conjunction with Libelium, are developing systems which involve monitoring the microclimate conditions of crops to predict crop health and the progression of plant diseases. With the use of wireless sensors and data analytics, the solutions can provide targeted treatments in order to keep the crops healthy, growing at optimal levels, and with minimal use of resources. A few attributes these sensors monitor include air temperature, humidity, leaf wetness and rainfall. In conjunction with weather reports, these statistics can better prepare growers about future problems. These systems also collect and keep historical data to adapt the systems to the unique characteristics of each grower’s land.
The data is then made available to people out in the field with the use of portable devices. Some growers have even chosen to make data about their crops available on online platforms so both wine growers and wineries have a better picture of the products they are producing and selling.
These types of solutions are helping vineyards be more profitable while lowering their impact on the surrounding environment.
WEARABLE TECHNOLOGY
Wearable Experiments – Sydney, Australia
Wearable Experiments has developed a jersey that lets a spectator feel what the players feel. What does this take? Real-time sports data being transmitted to a smartphone app, which is then connected to the electronics in the jersey. It is difficult to say if something like this will become main stream, but Cable TV companies are seeing customers unplug and sign up for streaming services which are more customizable to an individual’s needs. It is these types of technologies which will change the viewing experience and help attract/retain customers.
Technologies exist not only for spectators, but also for the players themselves. Football helmets have been designed with sensors which can measure and track head trauma. In some cases, players and trainers are not aware if a player has experienced anything series and the subject of injury, pain and long-term health is never brought up.
This use case is a good example of how different interests can prevent the implementation of new and immerging technologies. Do teams want these types of technologies when it means they lose control over the physical evaluation of their own players? And in like the retail example detailed at the beginning of this post, will consumers be willing to connect to retail store systems if they are aware their activities are being monitored?
PERSONAL SATELLITES
Ardu Sat – Salt Lake City, USA

IoT technology is transforming the classroom and changing the way teachers engage with their students. Ardu Sat is an open source Arduino based Nanosatellite. The general public is able to use the sensors aboard the satellite for their own purposes. People, teachers, and classrooms around the world are able to use the sensors to not only collect data, but also to share their data and the experiments they conduct.
Here are two sample experiments people are able to easily conduct with the use of these sensors.
- Calculating what generates less g-forces, an egg dropping in the sky attached to a parachute or an egg dropping with bubble wrap as a cushion.
- Letting students investigate the temperature changes which result from different altitudes with the use of a high altitude balloon.
The use cases provided in this post are a small sample of the things to come. Exactly what we can do and how long it takes is going to depend on a lot of factors: government regulation, public perception of the technology, access to enabling technologies, information security and consumer privacy just to name a few. However, things are already beginning to change, the technology is out there and people are going to continue coming up with innovative uses for both businesses and the general public.
______________________________________________________________
[i] [ii] [iii] Stroumboulopoulos, George. (16 August 2013). North America’s First All Digital Hospital is Coming to Toronto. CBC. Retrieved from http://www.cbc.ca/strombo/news/north-americas-first-all-digital-hospital-humber-river.html
© Discovered Intelligence Inc., 2016. Unauthorised use and/or duplication of this material without express and written permission from this site’s owner is strictly prohibited. Excerpts and links may be used, provided that full and clear credit is given to Discovered Intelligence, with appropriate and specific direction (i.e. a linked URL) to this original content.